Indian diaspora in Kuwait
- Indians have a significant presence in Kuwait. The Indian rupee was legal tender in Kuwait until 1961.
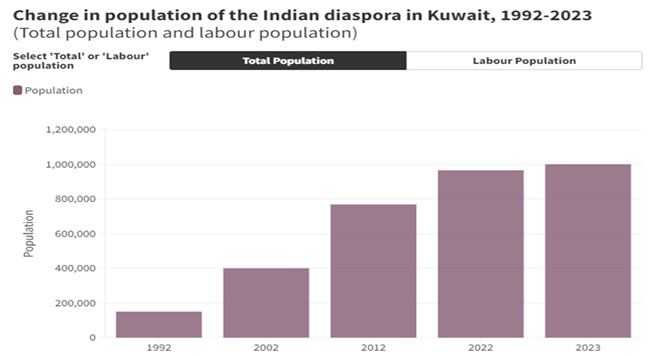
- Currently, around one million Indian diaspora live in Kuwait, making it the largest diaspora community in the country.
- According to the Indian Embassy, Indians constitute 21% of Kuwait’s total population and 30% of the total workforce.
- The Gulf War in the early 1990s had a significant impact on the Indian population in Kuwait, with over 1.7 lakh Indians returning to India.
- However, the number of Indians going to Kuwait gradually increased after the war.
- The Palestinian community was the largest diaspora community in Kuwait before the Liberation War in 1991, but their numbers declined and were overtaken by Indians.
- Kuwait is an important country for India from a manpower point of view. Yet as of July 2023, no strategic partnership existed between India and Kuwait.
Agreement between India and Kuwait
- India has also signed several bilateral agreements with Kuwait. According to the Indian Embassy in Kuwait, around 15 agreements/MoUs are in various stages of finalisation.
- The 15-year Bilateral Investment Promotion Agreement with Kuwait came into force on June 28, 2003, and expired on June 27, 2018.
What is the Gulf Cooperation Council
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is a group of six countries. Currently, the main source of revenue for these countries is oil export.
- The countries included in this group are:
- Saudi Arab
- United Arab Emirates
- Oman
- Kuwait
- Qatar
- Bahrain
- It was established in the year 1981 with the objective of promoting coordination, integration and inter-relationship among member countries on the basis of regional and cultural proximity.
- 25% of the Indian diaspora resides in 6 GCC countries and 56% of the NRIs (Non-Resident Indians) reside in these countries
Importance of GCC countries for India
- According to the Report of the Standing Committee of the Ministry of External Affairs on Cooperation between India and Gulf Cooperation Council, the region is an important source of remittances to India.
- The remittance from Indian emigrants is a very important dimension of the country’s economic development.
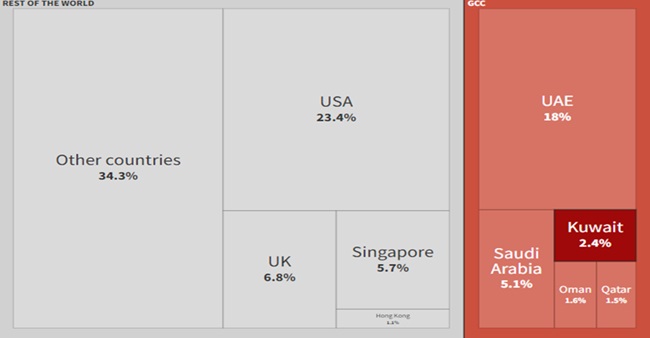
- The final figures for total remittances from abroad by NRIs and overall Indians were over $120 billion. India received 28.6% of the total foreign remittances from the GCC. Of this, remittances from Kuwait accounted for 2.4%.
- India was the highest recipient of remittances from abroad in the year 2022. The next remittance receiving countries are: Mexico > China > Philippines > France.
- A committee has recommended the Ministry of External Affairs to formulate a diaspora-centric policy focussing on the Gulf region for the welfare and protection of Indian emigrants in view of the potential for further increase in remittances.
Trade between India and Gulf countries
- According to the report of the Standing Committee on External Affairs, the GCC region accounts for nearly one-sixth of India’s total trade.
- India’s trade with these countries stood at around $184 billion in FY 2022-23 showing a growth of around 20% over the previous year.
- Currently the Indian government is also discussing a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the GCC countries.
- According to the Ministry of External Affairs, it is moving towards a comprehensive relationship with GCC countries in terms of energy cooperation by encouraging participation in India’s strategic petroleum reserves, negotiating long-term gas supply arrangements, obtaining concessions in oil fields and through renewable energy cooperation.
India and diaspora security
- Memorandum of Understanding on Labour, Employment and Manpower Development between India and Kuwait was signed in April 2007.
- India regulates migration with the more than 40-year-old Emigration Act, 1983, which puts migrant workers at risk. However, the Emigration Management Bill, 2022 is still pending.
- Expatriate welfare clause has been inserted in the Emigration (Amendment) Act, 2023.
- Similarly, India has not signed or ratified the International Labour Organisation Convention 189 or ILO C189 (Domestic Workers Convention), which provides domestic workers rights such as paid leave, minimum wages and employment contracts.
- India has also not signed or ratified the International Labour Organisation’s Convention 87 or ‘ILO C87’ (Freedom of association and protection of the right to organise). C87 guarantees freedom of association and protection of the right to organise.
- Although India has adopted the Global Compact for Migration, 2018, the Government of India has the sovereign right to decide who is a regular migrant and who is an irregular migrant.
COURTESY
https://www.sanskritiias.com/current-affairs/status-of-indian-migrants-in-gulf-countries-6